In the automotive industry, quality failures are not just costly but they can risk lives. That’s why top companies use FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) as a proactive tool to prevent problems before they reach the customer. This article explains the fundamentals and introduction to FMEA. Its purpose, how it works, and the benefits it brings to your quality processes.
Whether you’re designing a Motor, Gear, ECU or setting up a welding, assembly line, FMEA helps you to identify where failures might occur, why they happen, and how to control them effectively.
What is FMEA? #
The term Failure Modes and Effects Analysis means:
- Failure Modes: The ways in which something can fail.
- Effects: The consequences of those failures.
- Analysis: A systematic method to study and address them.

Simple Example:
- Component: Car battery.
- Failure Mode: Battery does not charge.
- Effect: Car will not start.
- Prevention Action: Stronger design, quality testing.
FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a structured, team-based method used to:
- Identify potential failure modes
- Analyze their causes and effects
- Evaluate the associated risks
- Prioritize actions to reduce risk
It is a preventive tool used during design and process development stages to produce a good quality and reliable product.
The AIAG-VDA FMEA Handbook defines FMEA as a,
"systematic group of activities intended to: recognize and evaluate the potential failure of a product or process, assess the risk associated, and identify actions that could eliminate or reduce the risk."
Purpose of FMEA #
The purpose of FMEA is to:
- Identify risks early in product or process development.
- Prioritize risks based on severity, occurrence, and detection.
- Implement preventive or corrective actions before customer impact.
- Support compliance with standards such as IATF 16949 and ISO 9001.
- Drive continuous improvement by linking lessons learned to future projects.
In simple words: FMEA helps you find weak points before your customer does.
Benefits of Using FMEA #
Applying FMEA provides multiple advantages for organizations. FMEA gives us powerful and technical risk analysis benefits when used into the product development stages:
1. Risk Mitigation
- Identifies what can go wrong before it happens
- Prioritizes high-severity, high-occurrence risks
- Make smart decision on corrective actions to those high risk failures.
2. Design & Process Improvement
- Strengthens design using DFMEA
- Improves process capability and reduces variation (PFMEA actions)
3. Cost Reduction
- Prevents costly rework, recalls, and warranty claims
- Reduces Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) at all stages
4. Compliance & Documentation
- Required by many OEMs and suppliers
- Provides structured documentation for PPAP, APQP, and audits
5. Cross-functional Collaboration
- Builds a culture of prevention over correction
- Encourages cross-departmental teamwork (Engineering, Quality, Production)
Comparison on what happen Before vs After FMEA
| Without FMEA | With FMEA |
|---|---|
| Failures found late in production | Risks identified in early design stage |
| High warranty costs | Reduced warranty claims |
| Poor customer confidence | Increased trust & satisfaction |
| Reactive firefighting | Proactive risk prevention |
Real-World Example from Automotive #
Design-FMEA Example:
Let’s say you’re developing a seatbelt tensioner system. In the DFMEA, the team identify:
- Failure Mode: Tensioner fails to activate during crash
- Effect: Passenger safety compromised
- Cause: Weak actuator spring or faulty sensor
- Action: Strengthen spring spec, add redundant sensor, validate under crash test simulation
Process-FMEA Example:
Imagine a welding process in an automotive plant:
- Failure Mode: Weld does not hold.
- Effect: Part breaks during use, causing safety issues.
- Prevention: Operator training, periodic testing, process control.
By performing a PFMEA (Process FMEA), the company can anticipate such risks and apply robust controls before full-scale production.
This proactive FMEA work avoids future safety risks, legal fines/penalties, and recalls.
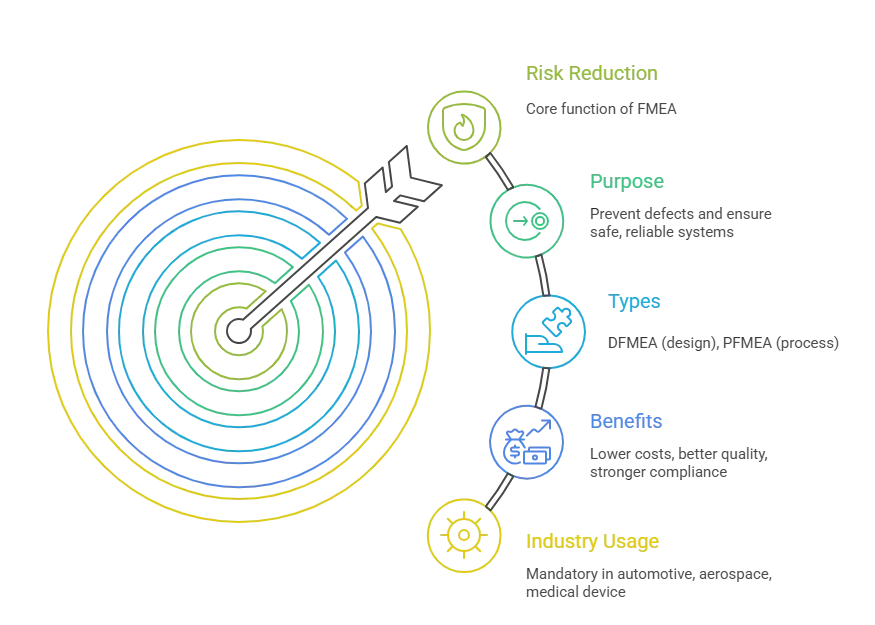
Summary #
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Definition | Tool to identify & reduce risk of failures |
| Purpose | Prevent defects and ensure safe, reliable systems |
| Types | DFMEA (design), PFMEA (process) |
| Benefits | Lower costs, better quality, stronger compliance |
| Industry Usage | Mandatory in automotive, aerospace, medical device |
While not legally required, FMEA is mandatory for automotive OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, especially under IATF 16949.
Start early in the design or process planning phase – It’s a preventive tool, not a corrective one.
DFMEA focusses on product design failures; PFMea focuses on manufacturing process failures.



